What Is Peripheral Neuropathy?
Peripheral neuropathy is a disease of the nerves. It most often starts in your feet. It may eventually affect the arms. It can affect sensory, motor, or both functions. It may cause pain or make you unable to sense pain. Sometimes weakness occurs as well. Lack of pain or loss of strength makes you more likely to injure yourself without knowing it. But you can learn ways to protect your feet from injury. Some neuropathies get worse very quickly and can be life-threatening.
Nerves that control bodily functions such as blood pressure, sweating, and heart rate are called autonomic nerves. Neuropathy can also affect these nerves and cause serious disability.
When nerves are diseased
Nerves in your feet carry signals to your brain. Your brain reads those signals and interprets them as sensations. When nerves in your feet are diseased, signals may be disrupted or changed. The result may be a lack of feeling (numbness) in your feet or other symptoms, such as tingling or pain.
Symptoms mask pain
Symptoms of peripheral neuropathy usually start in your toes. The symptoms may spread up your feet and legs as more nerve is affected. These symptoms may decrease sensation in your feet or mask pain. Without pain, you may not notice a cut or even a bone fracture. Cuts may become infected. Fractures may heal poorly and lead to foot deformity.
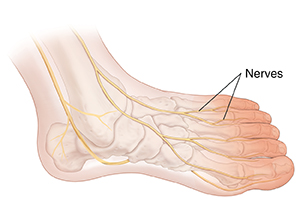 |
| Peripheral neuropathy symptoms often start in the toes and move up the foot. |
Common causes of peripheral neuropathy
Some common causes of peripheral neuropathy include:
-
Diabetes or other endocrine disorders
-
Toxins such as alcohol
-
Nutritional problems such as a lack of vitamin B-12
-
Kidney disease
-
Injury
-
Repetitive stress such as carpal tunnel syndrome
-
Autoimmune disease
-
Cancer and tumors
-
Chemotherapy cancer treatment
-
Hereditary disorders
-
Nervous system disorders
-
Infection
Diagnosis and treatment
Diagnosis of peripheral neuropathy includes a complete health history and physical exam. Blood tests and imaging tests often help find the cause. Special nerve tests are often helpful. These include nerve conduction velocity studies (NCV) and electromyography (EMG). NCV looks to see how well nerve signals are conducted. EMG helps tell whether symptoms are caused by muscle or nerve disorders. Genetic tests can be done if your healthcare provider suspects a hereditary neuropathy.
Treatment focuses on treating the underlying disorder and treating the symptoms. Treatment can include medicines, injections, TENS (transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation), acupuncture, and massage.
Online Medical Reviewer:
Anne Fetterman RN BSN
Online Medical Reviewer:
Joseph Campellone MD
Online Medical Reviewer:
Raymond Kent Turley BSN MSN RN
Date Last Reviewed:
8/1/2022
© 2000-2024 The StayWell Company, LLC. All rights reserved. This information is not intended as a substitute for professional medical care. Always follow your healthcare professional's instructions.